Topological Sort
Problem Statement
Return a topological ordering of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG).
Example: Graph with edges [[5,2],[5,0],[4,0],[4,1],[2,3],[3,1]] → [5,4,2,3,1,0]
Approach 1: DFS Post-order
Explanation: Perform DFS and add nodes to stack after exploring neighbors; reverse stack gives order.
Time Complexity: O(V + E)
Space Complexity: O(V) recursion stack
visited = set()
stack = []
function DFS(node):
visited.add(node)
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
if neighbor not visited:
DFS(neighbor)
stack.push(node)
for node in all_nodes:
if node not visited:
DFS(node)
return reversed(stack)
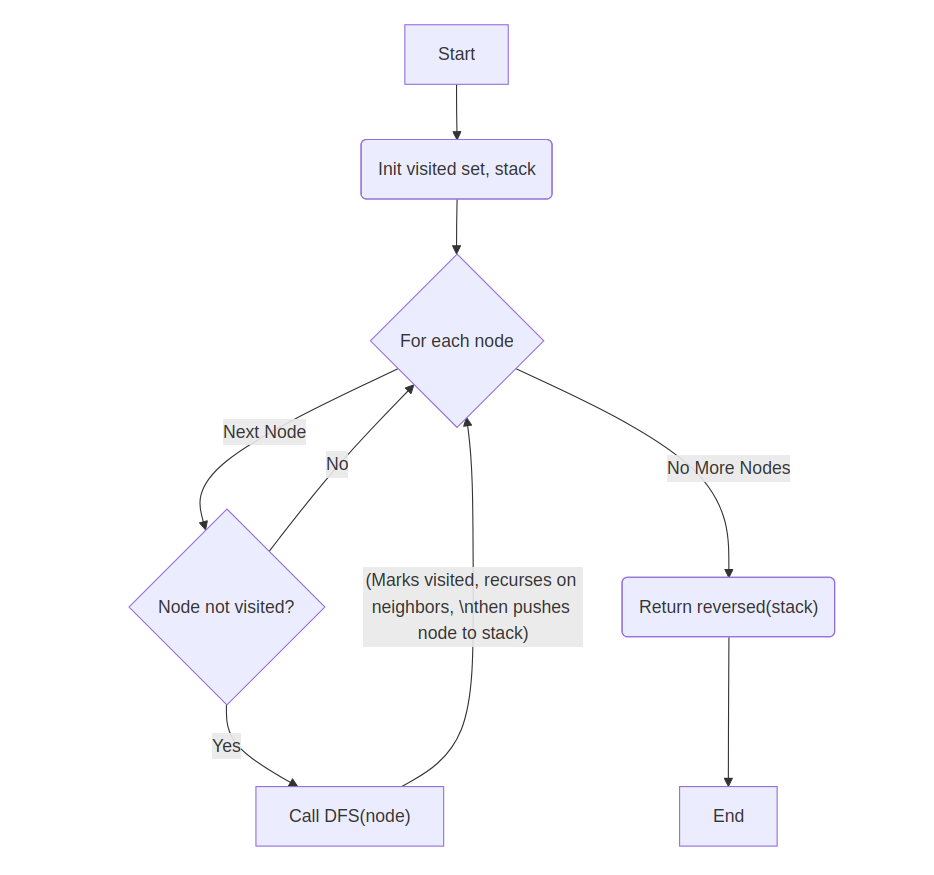
💡 Think: Finish times matter—push after exploring neighbors; reverse the stack for order.
Approach 2: Kahn’s Algorithm (BFS)
Explanation: Use in-degree array; push nodes with 0 in-degree into queue and update in-degrees.
Time Complexity: O(V + E)
Space Complexity: O(V)
in_degree = [0]*V
for u in all_nodes:
for v in u.neighbors:
in_degree[v] += 1
queue = nodes with in_degree 0
while queue not empty:
node = queue.pop()
result.append(node)
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
in_degree[neighbor] -= 1
if in_degree[neighbor]==0:
queue.push(neighbor)
return result
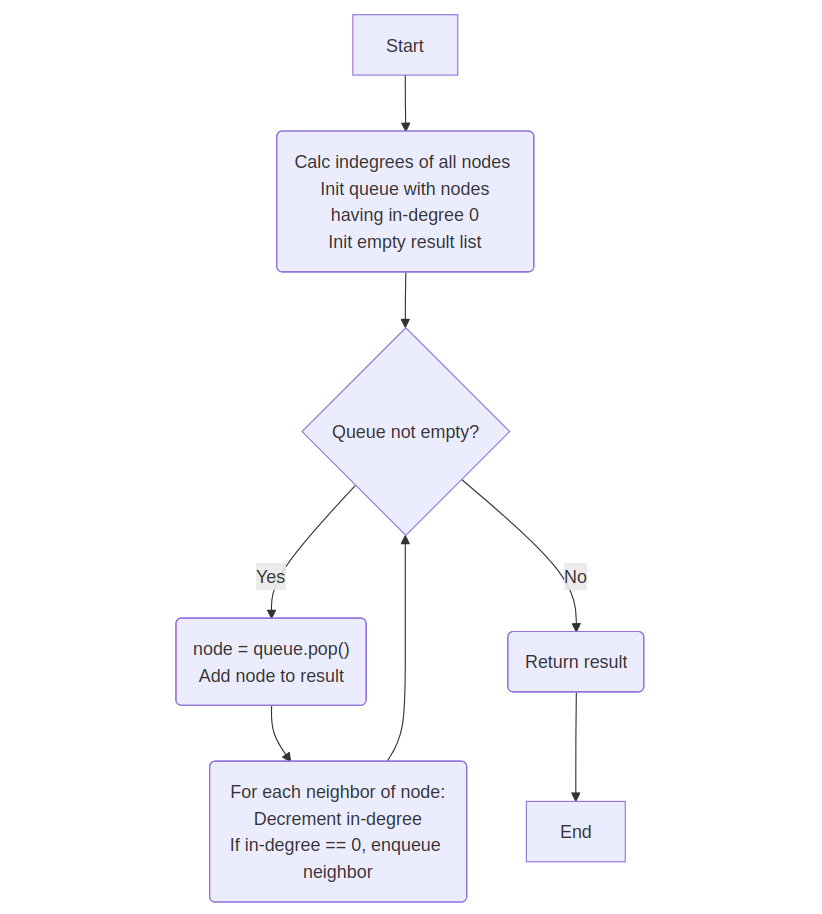
💡 Think: Peel nodes with in-degree 0 using a queue, decreasing in-degrees as edges are removed.