Shortest Path in Graph
Problem Statement
Find the shortest path from a source node to all other nodes in a weighted or unweighted graph.
Example: In an unweighted graph, source = 0 → shortest distances = [0,1,2,1,2,...]
Approach 1: BFS (Unweighted Graph)
Explanation: BFS ensures shortest path by layer-wise traversal in unweighted graphs.
Time Complexity: O(V + E)
Space Complexity: O(V)
dist = [∞]*V
dist[source] = 0
queue = [source]
while queue not empty:
node = queue.pop()
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
if dist[neighbor] == ∞:
dist[neighbor] = dist[node] + 1
queue.push(neighbor)
return dist
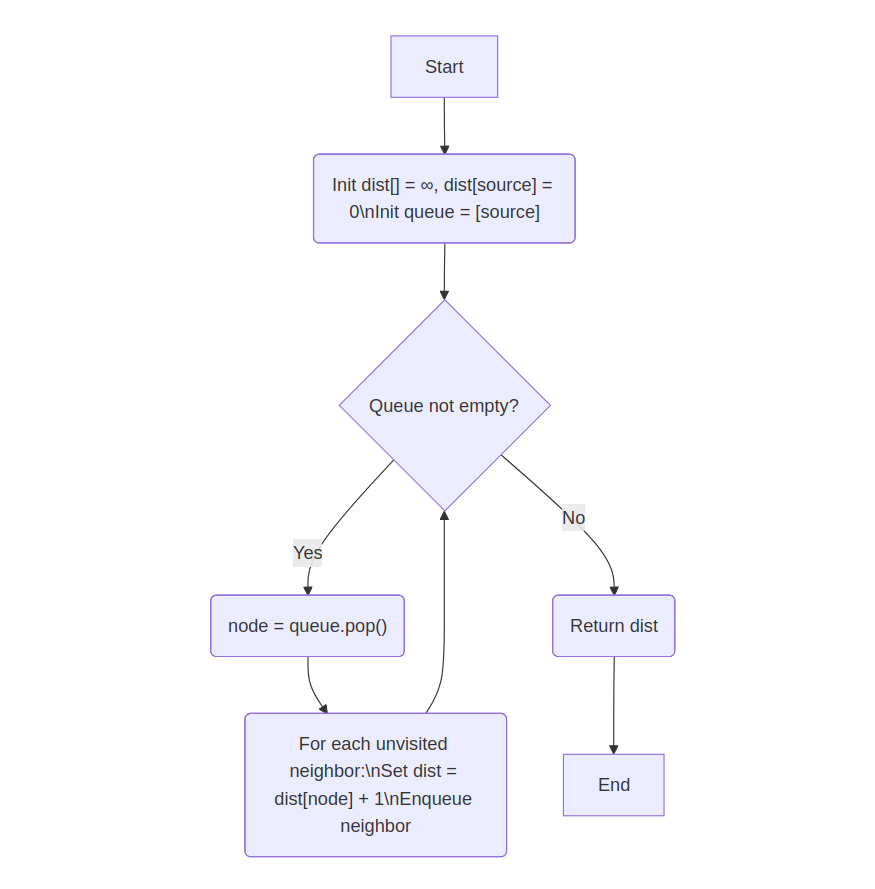
💡 Think: Layered expansion guarantees shortest hops; track distance by levels.
Approach 2: Dijkstra (Weighted Graph)
Explanation: Use min-heap to select the node with smallest distance iteratively in weighted graph with non-negative edges.
Time Complexity: O((V+E) log V)
Space Complexity: O(V)
dist = [∞]*V
dist[source] = 0
min_heap = [(0, source)]
while min_heap not empty:
(d, node) = heap.pop()
for neighbor, weight in node.neighbors:
if dist[node] + weight < dist[neighbor]:
dist[neighbor] = dist[node] + weight
heap.push((dist[neighbor], neighbor))
return dist
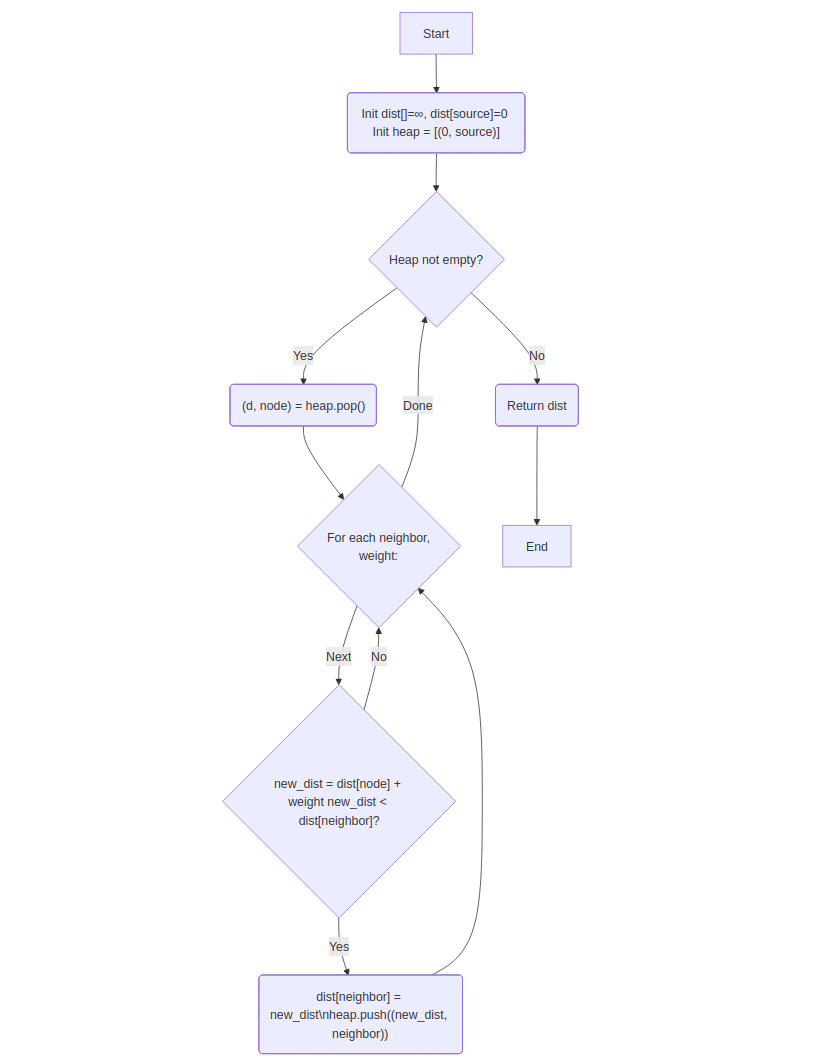
💡 Think: Greedily pick the smallest tentative distance via a min-heap and relax edges.
Approach 3: Bellman-Ford (Negative Weights)
Explanation: Relax all edges V-1 times; detects negative weight cycles.
Time Complexity: O(V*E)
Space Complexity: O(V)
dist = [∞]*V
dist[source] = 0
for i in 1..V-1:
for each edge (u,v,w):
if dist[u] + w < dist[v]:
dist[v] = dist[u] + w
check for negative weight cycles
return dist
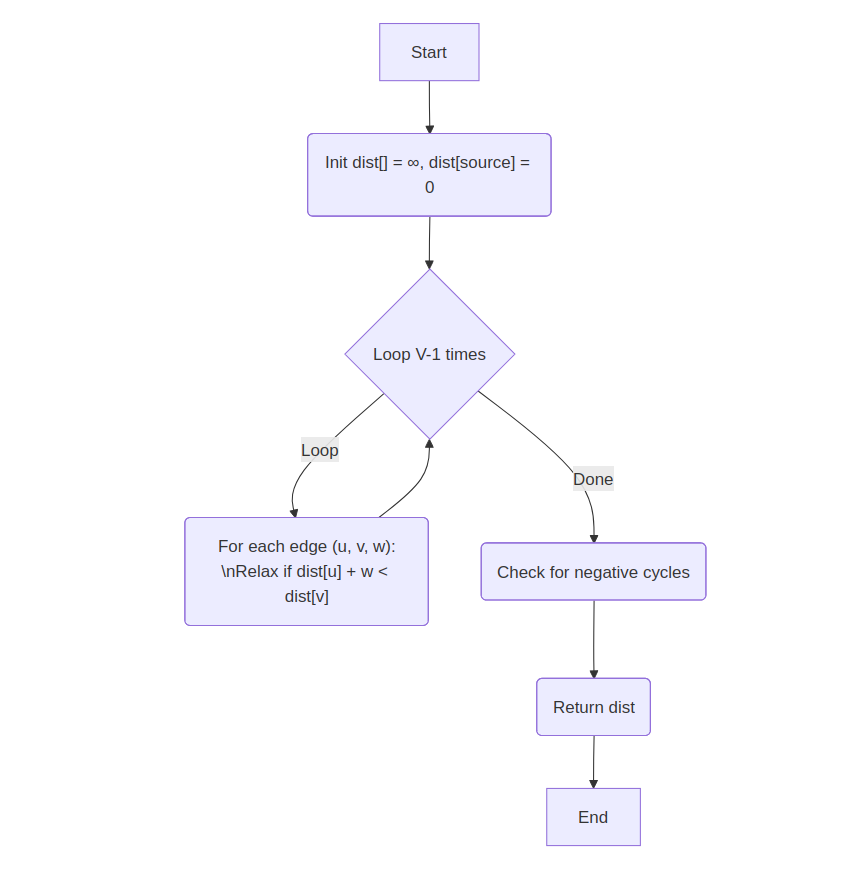
💡 Think: Relax all edges V−1 times and detect negative cycles on an extra pass.