Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)
Problem Statement
Find a tree connecting all nodes with minimum total edge weight in a connected undirected graph.
Example: Graph edges = [[0,1,4],[0,2,3],[1,2,1],[1,3,2],[2,3,4]] → MST total weight = 7
Approach 1: Kruskal’s Algorithm
Explanation: Sort edges by weight, add to MST if it doesn’t form cycle using Union-Find.
Time Complexity: O(E log E)
Space Complexity: O(V)
sort edges by weight
parent = [i for i in range(V)]
function find(x):
if parent[x] != x: parent[x] = find(parent[x])
return parent[x]
function union(x,y):
parent[find(x)] = find(y)
mst_weight = 0
for edge(u,v,w) in sorted edges:
if find(u) != find(v):
union(u,v)
mst_weight += w
return mst_weight
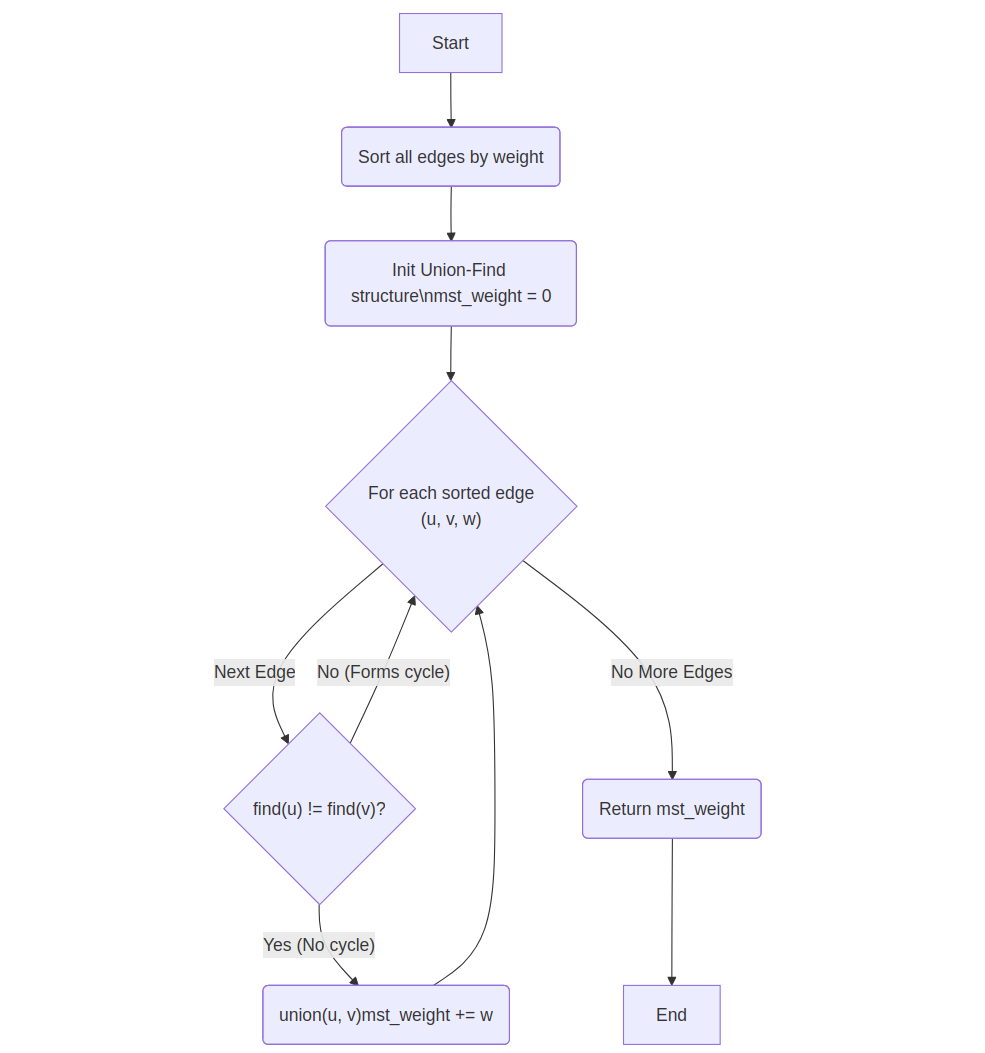
💡 Think: Sort edges; add the next lightest that doesn't form a cycle using DSU.
Approach 2: Prim’s Algorithm
Explanation: Start from a node, iteratively add smallest edge connecting MST to remaining nodes using min-heap.
Time Complexity: O(E log V)
Space Complexity: O(V + E)
visited = set()
min_heap = [(0, start_node)]
mst_weight = 0
while min_heap not empty:
(weight, node) = heap.pop()
if node in visited: continue
visited.add(node)
mst_weight += weight
for neighbor, w in node.neighbors:
if neighbor not in visited:
heap.push((w, neighbor))
return mst_weight
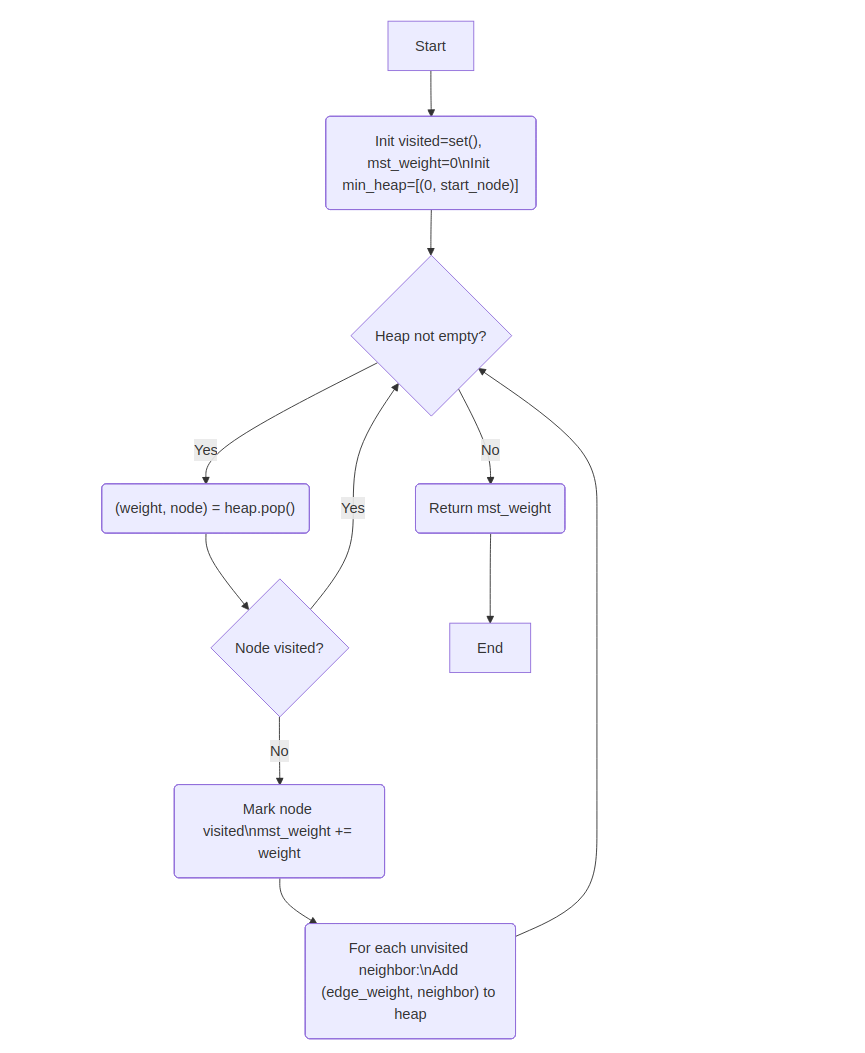
💡 Think: Grow from any node; pick the cheapest edge to a new node using a min-heap.