BFS & DFS Traversals
Problem Statement
Given a graph, traverse all nodes using BFS and DFS starting from a given node.
Example: Graph: 0→1,0→2,1→2,2→0,2→3 → BFS(0) = [0,1,2,3], DFS(0) = [0,1,2,3]
Approach 1: BFS (Queue)
Explanation: Use a queue to explore nodes level by level.
Time Complexity: O(V + E)
Space Complexity: O(V)
queue = [start]
visited[start] = true
while queue not empty:
node = queue.pop()
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
if neighbor not visited:
queue.push(neighbor)
visited[neighbor] = true
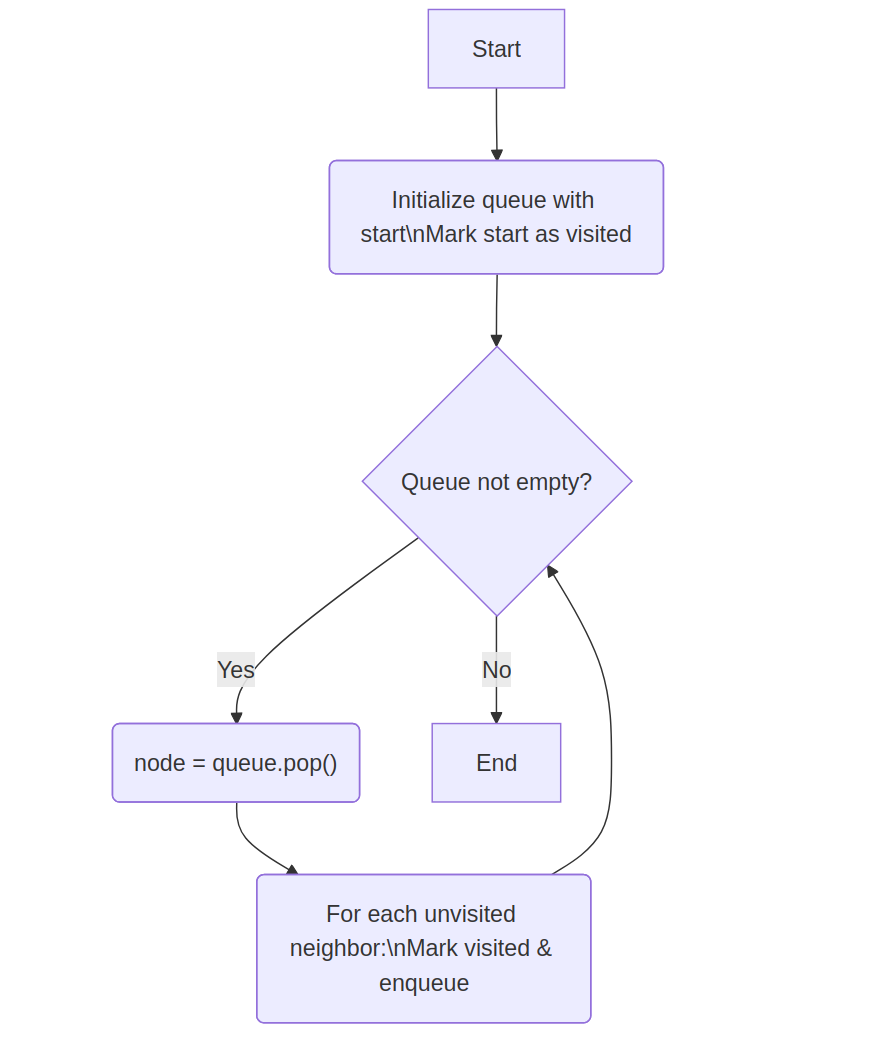
💡 Think: Explore level by level using a queue; enqueue unseen neighbors as you go.
Approach 2: DFS (Recursive)
Explanation: Recursively visit neighbors using a visited set.
Time Complexity: O(V + E)
Space Complexity: O(V) (recursion stack)
function DFS(node):
visited[node] = true
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
if neighbor not visited:
DFS(neighbor)
DFS(start)
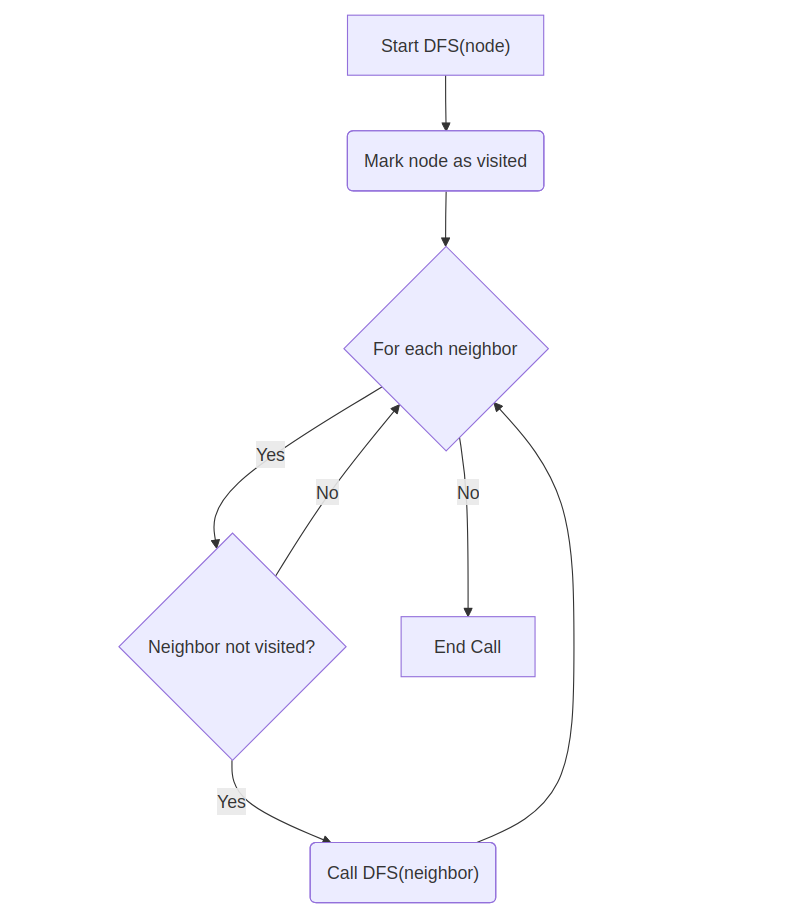
💡 Think: Dive deep along one path via recursion, backtrack when stuck using a visited set.
Approach 3: DFS (Iterative)
Explanation: Use a stack to simulate recursion.
Time Complexity: O(V + E)
Space Complexity: O(V)
stack = [start]
visited[start] = true
while stack not empty:
node = stack.pop()
for neighbor in node.neighbors:
if neighbor not visited:
stack.push(neighbor)
visited[neighbor] = true
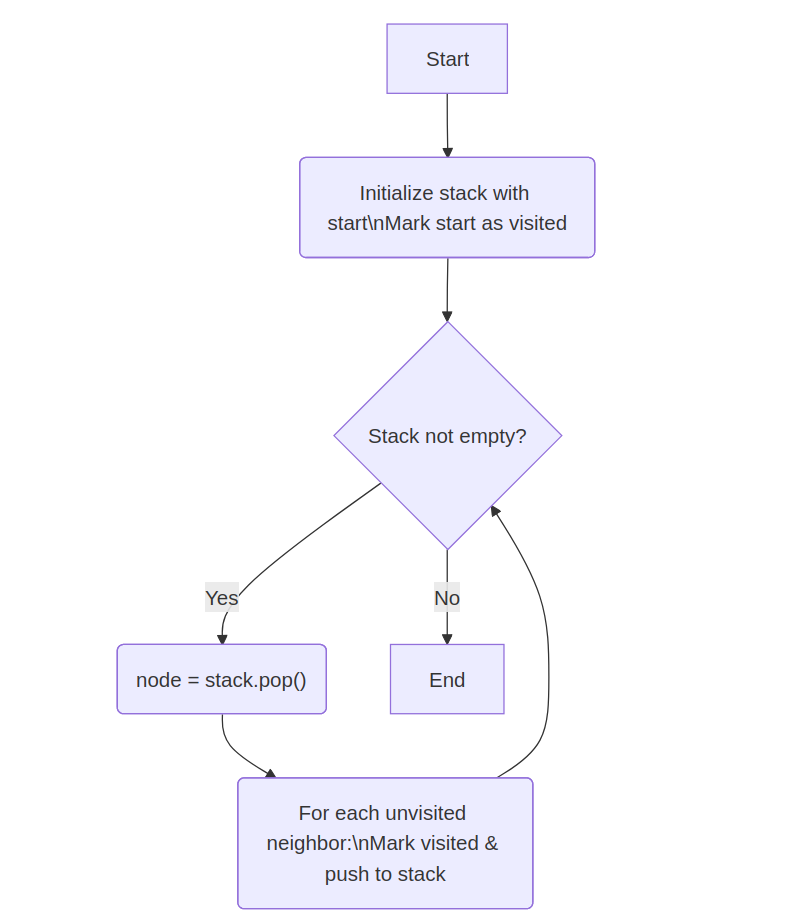
💡 Think: Use an explicit stack to mimic recursion, pushing neighbors and exploring depth-first.