Unbounded Knapsack
Problem Statement
Given n items with weights wt[] and values val[], and a knapsack capacity W, determine the maximum total value you can obtain. You can use **each item multiple times**.
Example: Input: W = 8, wt = [2,3,5], val = [50,100,140], Output: 300 (take two 3-weight items and one 2-weight)
Approach 1: Recursion
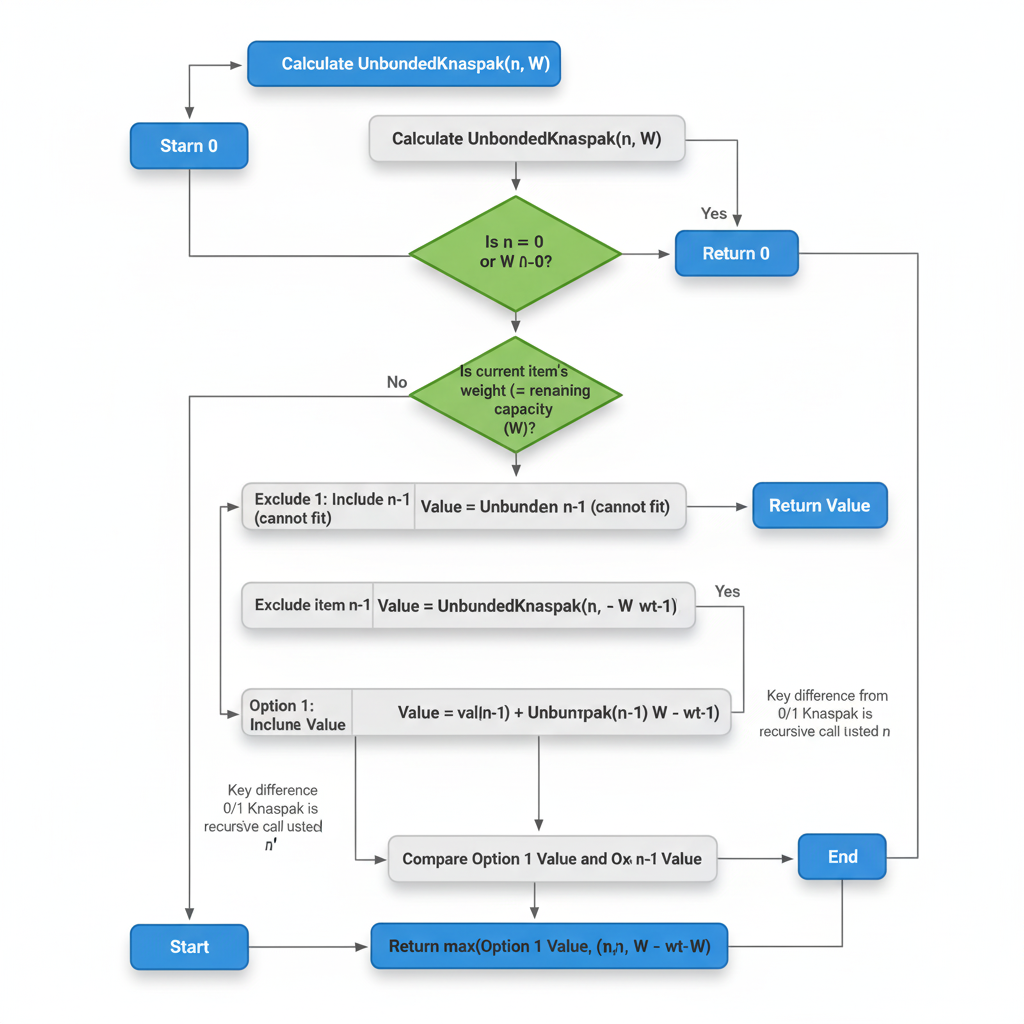
Explanation: For each item, decide how many times to include it (0 to W/wt[i]) recursively.
Time Complexity: Exponential
Space Complexity: O(n) recursion stack
function UnboundedKnapsack(W, n):
if n == 0 or W == 0: return 0
if wt[n-1] <= W:
return max(
val[n-1] + UnboundedKnapsack(W - wt[n-1], n),
UnboundedKnapsack(W, n-1)
)
else:
return UnboundedKnapsack(W, n-1)
💡 Think: Allow reusing an item by staying on the same i when you include it.
Approach 2: Memoization (Top-Down DP)
Explanation: Store results for subproblems (W, n) to avoid recomputation.
Time Complexity: O(n * W)
Space Complexity: O(n * W) DP array + O(n) recursion stack
dp[0..n][0..W] = -1
function UnboundedKnapsack(W, n):
if n == 0 or W == 0: return 0
if dp[n][W] != -1: return dp[n][W]
if wt[n-1] <= W:
dp[n][W] = max(
val[n-1] + UnboundedKnapsack(W - wt[n-1], n),
UnboundedKnapsack(W, n-1)
)
else:
dp[n][W] = UnboundedKnapsack(W, n-1)
return dp[n][W]
💡 Think: Memoize (i,W) with the include-same-item transition.
Approach 3: Tabulation (Bottom-Up DP)
Explanation: Iteratively fill DP table where dp[i][w] represents max value using first i items for weight w.
Time Complexity: O(n * W)
Space Complexity: O(n * W)
dp[0..n][0..W] = 0
for i = 1 to n:
for w = 0 to W:
if wt[i-1] <= w:
dp[i][w] = max(val[i-1] + dp[i][w - wt[i-1]], dp[i-1][w])
else:
dp[i][w] = dp[i-1][w]
return dp[n][W]
💡 Think: dp[i][w] considers taking item i multiple times vs skipping it.
Approach 4: Space Optimization
Explanation: Use a 1D DP array, update dp[w] for each item to save space.
Time Complexity: O(n * W)
Space Complexity: O(W)
dp[0..W] = 0
for i = 0 to n-1:
for w = wt[i] to W:
dp[w] = max(dp[w], val[i] + dp[w - wt[i]])
return dp[W]
💡 Think: Iterate w increasing so dp[w] can reuse dp[w - wt[i]] for unlimited picks.