0/1 Knapsack Problem
Problem Statement
Given weights wt[] and values val[] of n items, and a maximum weight W, find the maximum total value of items that can be included in the knapsack without exceeding the weight limit. Each item can be included at most once.
Example: Input: val = [60, 100, 120], wt = [10, 20, 30], W = 50, Output: 220
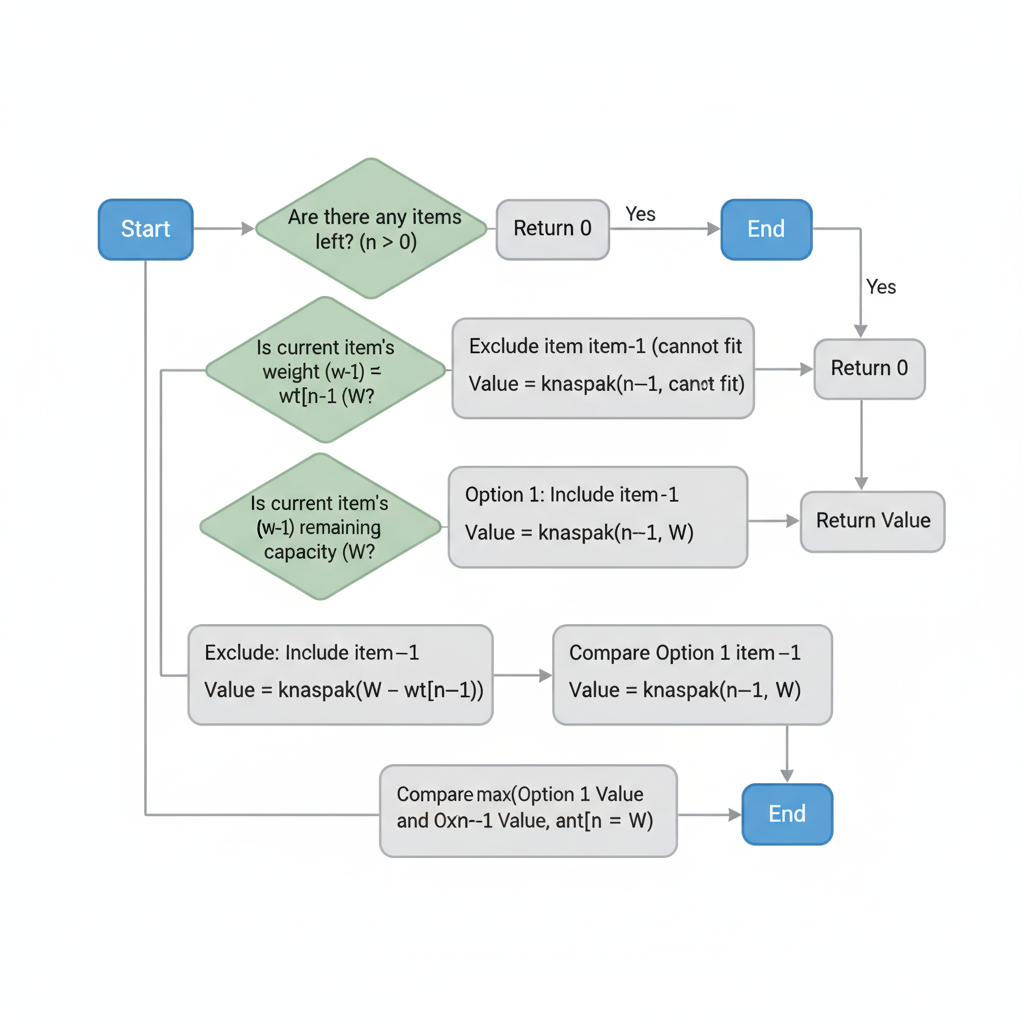
Approach 1: Recursion
Explanation: Consider two choices for each item: include or exclude.
Time Complexity: O(2n)
Space Complexity: O(n) recursion stack
function knapsack(n, W):
if n == 0 or W == 0: return 0
if wt[n-1] > W:
return knapsack(n-1, W)
return max(
val[n-1] + knapsack(n-1, W - wt[n-1]),
knapsack(n-1, W)
)
💡 Think: For each item, choose include or exclude and take the better value.
Approach 2: Memoization (Top-Down DP)
Explanation: Store results for subproblems (n, W) to avoid recomputation.
Time Complexity: O(n*W)
Space Complexity: O(n*W) + O(n) recursion stack
dp = array of size n+1 x W+1, initialized to -1
function knapsack(n, W):
if n == 0 or W == 0: return 0
if dp[n][W] != -1: return dp[n][W]
if wt[n-1] > W:
dp[n][W] = knapsack(n-1, W)
else:
dp[n][W] = max(
val[n-1] + knapsack(n-1, W - wt[n-1]),
knapsack(n-1, W)
)
return dp[n][W]
💡 Think: Store (i,W) subproblem results to avoid recomputing branches.
Approach 3: Tabulation (Bottom-Up DP)
Explanation: Fill DP table iteratively for all weights and items.
Time Complexity: O(n*W)
Space Complexity: O(n*W)
dp[0..n][0..W] = 0
for i = 1 to n:
for w = 1 to W:
if wt[i-1] <= w:
dp[i][w] = max(dp[i-1][w], val[i-1] + dp[i-1][w - wt[i-1]])
else:
dp[i][w] = dp[i-1][w]
return dp[n][W]
💡 Think: Fill a 2D dp of items vs capacity, reusing previous-row answers.
Approach 4: Space Optimized DP
Explanation: Use 1D array instead of 2D to save space.
Time Complexity: O(n*W)
Space Complexity: O(W)
dp[0..W] = 0
for i = 0 to n-1:
for w = W down to wt[i]:
dp[w] = max(dp[w], val[i] + dp[w - wt[i]])
return dp[W]
💡 Think: Scan weights backward so each item is used at most once in 1D dp.