Maximum Path Sum
Problem Statement
Given a non-empty binary tree, find the maximum path sum. A path is defined as any sequence of nodes from some starting node to any node in the tree along the parent-child connections. The path must contain at least one node and does not need to go through the root.
Example:
Input: 1
/ \
2 3
Output: 6 (2 → 1 → 3)
Approach 1: Recursive DFS with Global Max
Explanation: At each node, compute max path sum including left/right children. Update global maximum including both sides.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(h) (recursion stack, h = tree height)
maxSum = -∞
function maxPathSum(node):
if node == NULL: return 0
left = max(0, maxPathSum(node.left))
right = max(0, maxPathSum(node.right))
maxSum = max(maxSum, node.val + left + right)
return node.val + max(left, right)
return maxSum
💡 Think: At each node take max(0,left), max(0,right); update global with node+left+right.
Approach 2: Iterative Postorder DFS
Explanation: Use a stack for postorder traversal. Track max path sum at each node using a hashmap to store results of left/right children.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n) (stack + hashmap)
stack = [(root, False)]
maxMap = {}
maxSum = -∞
while stack:
node, visited = stack.pop()
if node is NULL: continue
if visited:
left = max(0, maxMap.get(node.left,0))
right = max(0, maxMap.get(node.right,0))
maxSum = max(maxSum, node.val + left + right)
maxMap[node] = node.val + max(left, right)
else:
stack.push((node, True))
stack.push((node.right, False))
stack.push((node.left, False))
return maxSum
💡 Think: Compute child gains via stack map; update global when visiting node.
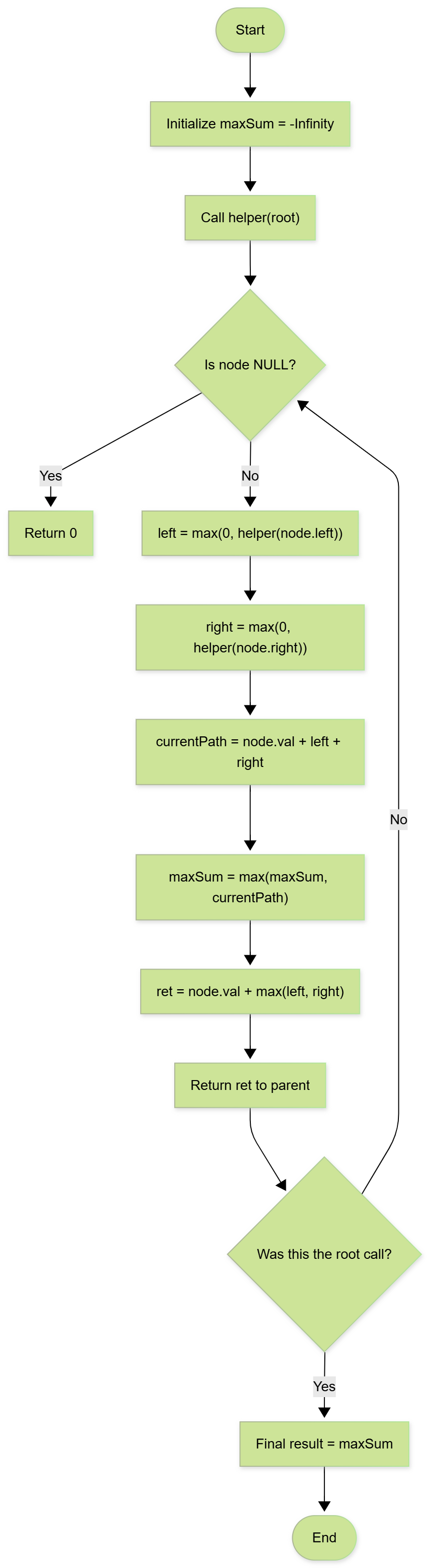
Approach 3: DFS with Return Values Only
Explanation: Recursive DFS returns max sum for parent-child path. Global variable tracks overall max including both children.
Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(h)
maxSum = -∞
function helper(node):
if node == NULL: return 0
left = max(0, helper(node.left))
right = max(0, helper(node.right))
maxSum = max(maxSum, node.val + left + right)
return node.val + max(left, right)
helper(root)
return maxSum
💡 Think: Return single-branch gain upward; track best split-path in a global.